Welcome to visitShanghai Chinon medical Model & Equipment Manufacturing Co., LTD
With the continuous development and refinement of global medical education, the requirements of medical training equipment are gradually increasing. Especially for high-precision educational tools, the medical profession has increasingly high expectations for their quality, functionality, and adaptability. As an important anatomical and clinical teaching tool, whether skull model can adapt to the global market demand for high-precision medical education equipment has become a hot topic in the industry and academia.
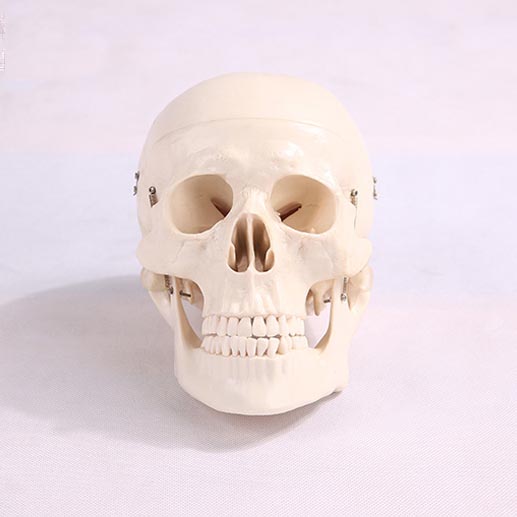

1. The precision requirements of training equipment: the cornerstone of fine teaching
Modern medical education not only requires students to master basic anatomy knowledge, but also needs them to have a high degree of precision operation ability. As the basic tool of anatomy, the precision of skull model is increasingly strict. Traditional skull models may not fully meet the needs of high-precision teaching, especially when it comes to showing details (such as the connection of tiny bones, the distribution of nerves and blood vessels, etc.). With the development of 3D printing technology and advanced material technology, skull models can present higher detail and accuracy. For example, it is possible to accurately reproduce every detail of the skull, anatomical differences between different ages, and even to customize disease models (such as brain injury or fracture simulations) through modular design. These technological advances allow skull models to better adapt to the global market demand for high-precision medical education devices.
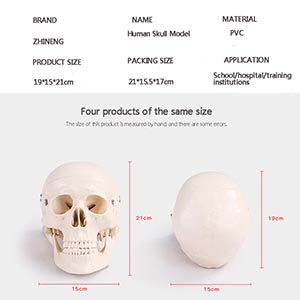
2. Market trends: Education and clinical needs driven by both directions
Global medical education is in a period of transition, especially in terms of the increasing demand for high-precision teaching tools and simulation technologies. With the rapid development of medical technology, medical professional training requires students not only to master the basic theory, but also to have a strong clinical operation ability. The skull model came into being, which not only serves the anatomy study of medical students, but also provides support for the surgical training of clinicians. There is a growing demand for educational devices that can highly simulate reality. For example, as the complexity of surgical procedures continues to increase, three-dimensional models that simulate real skulls are increasingly favored by surgeons and medical training institutions.
Data show that the global medical training equipment market is growing at a rate of about 5% per year, especially high-precision, interactive analog equipment demand is the strongest. Skull models will play an important role in this context, by providing a more accurate display of anatomical structures, to meet the needs of medical training and continuing education.
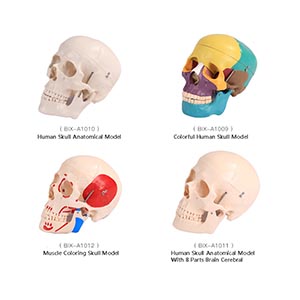
3. Professional application: from basic education to advanced clinical training
The market for skull models is not limited to the field of medical education, it is also widely used in various professional training scenarios. For example, neurosurgeons, oral surgeons, and plastic surgeons, among others, all need to be trained for surgery with high-precision models. Skull models are able to provide a full range of support from basic anatomical learning to complex surgical practice, which makes them in a wide range of professional areas of market demand.
In oral surgery training, skull model can help students understand the relationship between teeth and bones, and perform tooth extraction, implantation, root canal treatment and other operations. In the field of neurosurgery, the model can help students learn how to perform brain surgery, ensuring that the training process is highly realistic.
4. Data-driven: real-time feedback improves learning efficiency
Modern skull models not only have highly accurate anatomical structures, but also provide real-time feedback in combination with data analysis techniques. Through sensors, artificial intelligence or machine learning algorithms, the model is able to record the student's operational data, such as the force, Angle, order of operation, and so on, analyze the student's errors and provide suggestions for correction. Data-driven training can greatly improve the learning efficiency of students, so that they can master clinical skills faster and reach a higher level of training.
This personalized learning style based on data feedback not only helps students improve their skills, but also helps teachers assess students' learning progress in real time and adjust teaching strategies according to students' needs. With the development of data analysis technology, the accuracy and intelligence level of skull models will continue to improve to meet the needs of more and more medical professionals and teaching institutions.
Skull models show strong adaptability and development potential in the context of the increasing demand for high-precision medical education equipment in the global market. With advanced manufacturing technologies, such as 3D printing and virtual reality, the skull model can not only provide a detailed anatomical display, but also support clinical operation training to meet the needs of different medical specialties and educational institutions. With the continuous advancement of data analysis technology and personalized teaching, skull models will better support students' clinical skills training and help medical education be more accurate and efficient. Therefore, skull models are expected to become an important part of the global medical education equipment market, driving the development of medical training and clinical skills education.