Welcome to visitShanghai Chinon medical Model & Equipment Manufacturing Co., LTD
In medical education, anatomy is an important part of basic medicine, and the anatomical study of upper limb muscles is crucial to the clinical operation skills of medical students. With the continuous innovation of teaching methods, teaching model, especially the anatomical model of upper limb muscle, has become an indispensable tool in medical education. Through these detailed three-dimensional anatomical models, students can not only gain an in-depth understanding of the structure of the upper limb muscles, but also obtain more intuitive and precise training in a variety of clinical operations, thereby improving their clinical skills, especially in surgery, physical therapy and rehabilitation training.
1. Improve anatomical cognition and operation accuracy
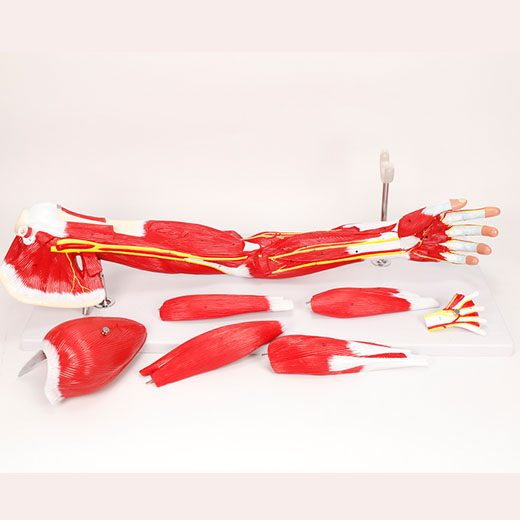

Upper Limb Muscle Anatomy Model
The anatomical model of upper limb muscle provides a vivid and intuitive learning platform for medical students. In traditional anatomy teaching, students often rely on book illustrations or autopsies, and these methods lack a dynamic understanding of muscle groups and their functions. Through the three-dimensional upper limb muscle model, students can observe the spatial relationship between muscles, tendons, ligaments and other structures in an all-round way, and grasp the specific role of each muscle in limb movement.
For example, students can use the model to compare the starting parts, attachment points and functions of different muscle groups in the upper limb, and to determine the muscle direction, contraction pattern and interaction with the bone of the biceps, triceps and forearm muscles. This three-dimensional structure helps students to master the operation skills more accurately, especially in the operation of intramuscular injection, physical therapy, rehabilitation training, etc., to ensure the accuracy of muscle positioning and reduce the risk of misoperation.
2. Enhance the interaction of clinical skill training
The anatomical model of upper limb muscle not only helps students master theoretical knowledge, but also improves their interaction ability in practice. Students can perform a variety of simulation operations on the model, such as simulated muscle massage, muscle stretching and functional testing of muscle groups. By practicing these operations repeatedly, students are able to familiarize themselves with the changes in muscle structure during different movements and quickly apply them to the clinic.
For example, in physical therapy, students can model different rehabilitation movements, such as shoulder abduction and rotation, elbow flexion and extension, to better understand the traction and stretching effects of these movements on muscle groups. The palpation and positioning of simulated muscle groups can help students perform clinical operations more accurately and provide a reliable basis for future rehabilitation treatment.
3. Promote the improvement of clinical diagnosis and treatment skills

In the learning process of upper limb muscle anatomy, the anatomical model provides a practical platform for clinical diagnosis and treatment. With an in-depth understanding of muscle structure, students are able to more clearly identify the types of muscle injuries and dysfunction, thus improving diagnostic accuracy. For example, models can help students understand the different types of disease manifestations such as muscle strain, tendon rupture, or muscle atrophy, and how these lesions affect a patient's motor function.
Studies have shown that using muscle anatomy models to simulate operations can improve students' decision-making ability in clinical practice. For example, a 2018 study showed that students trained with muscle models showed greater accuracy and agility in muscle assessment and diagnosis compared to traditional teaching methods (source: Journ of Clinical Anatomy). This indicates the effectiveness of the model in improving clinical operation skills, especially in muscle function assessment, rehabilitation training plan development and muscle injury diagnosis.
4. Data support: The role of the model in improving students' clinical skills
Several studies have shown that anatomical models can significantly improve the clinical skills of medical students. For example, a study of Medical students (source: Medical Education, 2020) found that students who were trained using 3D muscle models showed greater accuracy and confidence in practical practice than students with traditional teaching methods. The study's statistics showed that students trained with the model improved their accuracy in muscle group positioning, physical therapy, and intramuscular injections by about 15 to 20 percent.
In addition, another study on the effect of model teaching on Clinical Skills (Source: Journal of Clinical Skills, 2021) showed that students using anatomical models of upper limb muscles improved their proficiency and accuracy in muscle function assessment and limb movement training by about 25% compared to students taught in traditional classrooms. The use of models not only makes it easier for students to master complex muscle structures, but also promotes their ability to react quickly and operate in real clinical scenarios.
5. Improve students' hands-on ability and spatial cognition
As an operable and interactive learning tool, the upper limb muscle anatomy model can effectively improve students' hands-on ability and spatial cognitive ability. In clinical practice, the precise entry point of surgery, the precise positioning of muscles, and the execution of movement therapy all depend on the spatial perception of the doctor or therapist. Through repeated practice of limb model, students can more clearly understand the spatial distribution of muscle structure, so as to make quick and accurate judgment in operation, treatment and other operations.
Conclusion
Overall, the upper limb muscle anatomy model is a vital tool in medical education, and through its application, students are able to better understand the structure and function of muscles, thereby improving clinical manipulation skills. The model not only contributes to the deepening of theoretical learning, but also promotes the accurate improvement of clinical skills, especially in muscle positioning, physical therapy, rehabilitation training and other aspects of its unique value. Through systematic training and data support, the teaching model has become an important asset in medical education, helping to train higher level clinical professionals.